Oxolamine citrate
CAS No. 1949-20-8
Oxolamine citrate( Oxalamine Citrate | Oxalamine Citrate salt )
Catalog No. M13049 CAS No. 1949-20-8
Oxolamine is a cough suppressant that is available as a generic drug in many jurisdictions.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 200MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 45 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameOxolamine citrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionOxolamine is a cough suppressant that is available as a generic drug in many jurisdictions.
-
DescriptionOxolamine is a cough suppressant that is available as a generic drug in many jurisdictions.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsOxalamine Citrate | Oxalamine Citrate salt
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1949-20-8
-
Formula Weight437.44
-
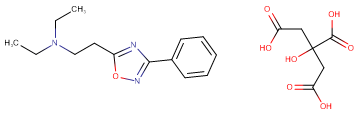
Molecular FormulaC14H19N3O·C6H8O7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 10 mM
-
SMILESCCN(CC)CCC1=NC(C2=CC=CC=C2)=NO1.OC(C(O)=O)(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O
-
Chemical NameN,N-Diethyl-2-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)ethanamine citrate
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Ceyhan BB, Karakurt S. Respir Med. 2002 Jan;96(1):61-3.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Methyl 5-hydroxypyri...
Methyl 5-hydroxypyridine-2-carboxylate is a phenolic acid that can found in the stems of Mahonia fortune . Methyl 5-hydroxypyridine-2-carboxylate exhibits NO inhibitory effects in vitro.
-
P-SCN-Bn-DOTA
p-SCN-Bn-DOTA is a chelator that simultaneously binds radionuclides and links monoclonal antibodies.
-
2-AMINO-5-PHENYL-THI...
2-AMINO-5-PHENYL-THIOPHENE-3-CARBOXYLIC is an inhibitior of IKKβ.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


